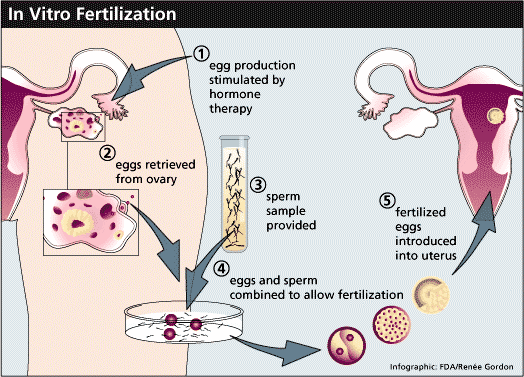
A mature egg is obtained from the ovary and mixed with thousands of the husband’s sperm in a special lab dish under appropriate environmental conditions simulating the natural state. The process of fertilization is monitored in the lab until fertilization is complete and cellular division of the egg (embryo) has begun, after which the egg is returned to the mother’s uterus via the cervix.
When do we resort to the test tube baby?
We do so in the following cases:
• The woman’s fallopian tubes are blocked (tubal factor).
• The woman has irregular periods (anovulatory cycles).
• The man has sperm that is low in terms of number, motility or shape (oligoasthenoteratospermia).
• Unexplained infertility.
• Presence of antibodies against sperm (antisperm antibodies).
What is Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) or microinjection of the egg?
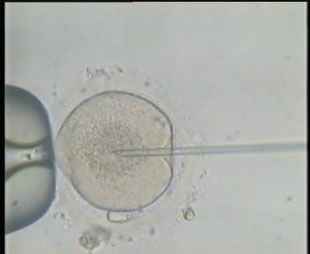
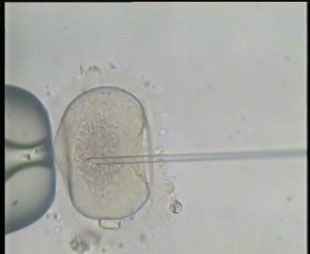
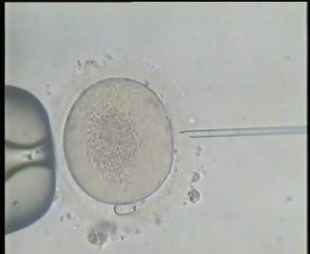
It is the process of injecting a single sperm into a mature egg by introducing the sperm in the nucleus of the egg using a microscopic needle (diameter 7 microns) without affecting the viability of the egg. The fertilized egg is then monitored until it starts to divide forming the embryo after which it is returned to the mother’s uterus via the cervix.
Who is in need of (ICSI)?
• Very low sperm counts or motility (severe oligoastherospermia).
• Absence of sperm in the seminal fluid due to obstruction or congenital absence of the tubes carrying sperm from the testes (Obstructive Azoospermia).
• In cases of internal ejaculation into the urinary bladder (Retrograde Ejaculation).
• Failure of classical IVF.
How does Fertilization occur outside the body?
The woman is injected with drugs that stimulate the ovaries to produce several eggs (ovulation induction). During the course of treatment, which takes several days, she visits the clinic regularly where progress of treatment is monitored by determining the number and size of eggs formed in the ovaries, as well as the levels of the hormones produced by the ovaries, namely Estradiol and Progesterone.
This is done in the operating room under light general or local anesthesia by one of two methods:
1. Transvaginal egg collection (the usual method).
2. Laparoscopic egg collection (rare).
Fertilization and Incubation of eggs:
After the eggs are retrieved, they are fertilized by either classical IVF or ICSI as described above. The eggs are then placed in a special incubator and their development into embryos is observed over 2-3 days. At that point and depending on several factors such as age of the woman, previous history, etc., anywhere between 1 and 4 embryos are placed in the woman’s uterus via the cervix (Embryo Transfer or ET).
The woman then follows a treatment plan for 2 weeks to encourage implantation and pregnancy after which a blood pregnancy test is performed. The next step depends on the result of this test.
It is noted that some patients experience a small amount of bleeding due either to the returning of the embryos to the uterus or their implantaion therein.
This is not to be confused with menstrual bleeding, and should not be a cause of anxiety.
What is the percentage of success?
A number of factors contribute to the success. However, in the best conditions and with all the modern technology the percentage of success now approaches 40%; previously it used to be no more than 17%. The current results in our unit approximate 30% .
The percentage of successful deliveries is 20% per attempt, the percentage increasing with the increase in number of trials.
Congenital malformations
Studies have show that the percentage of congenital malformation in IVF pregnancies is similar to that in spontaneous pregnancies (2-5%).
Factors affecting success of the test tube baby
1. The woman’s age is a major and important factor. It is known that the conception decreases significantly in women above 40 rate.
2. Number and quality of both eggs and sperm.
3. The quality and number of embryos formed, the success rate increasing correspondingly.
4.The expertise of the medical team supervising ovulation induction and egg retrieval, as well as that of the laboratory team involved in fertilizing and incubating the eggs, are considered among the most important of factors in the success of IVF.